After covering the traditional financial markets in the first part of this series, we now move on to the revolution of digital assets. In this article, we explore the origins of digital assets, highlight their subcategories, and in particular, the different types of cryptocurrencies.
How it all started: Blockchain & DLT
The first major breakthrough with blockchain technology is the now-famous Bitcoin – a digital currency developed and reliant on this new technology. Essentially, the blockchain is a cryptographically secured and verified collection of groups (blocks) of transactions with the innovation being the ability to eliminate the double-spending problem. The blockchain has since been discovered to prove more and more useful, with its applications branching out into other fields. Smart contracts are another example use of this technology.
Blockchain is an example of something more general, called Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT). A DLT is simply a decentralized database that is managed and agreed upon by its various users. There is no central authority, or third party acting as arbitrator or monitor, allowing for smoother, faster, and cheaper transactions. As the name suggests, it is a distributed log of records that every user has and shares a consensus over, meaning there is greater transparency – making fraud and manipulation more difficult. With the cryptographic technology supporting it, it is also more difficult for hackers to target.
Depending on the type of blockchain, parties may be able to view previous ledger entries and record new ones (public blockchain) or not (private blockchain). However, the addition of new groups of records, called blocks, to the chain of previous records is a complex process that follows specific and strict rules that can differ between blockchain networks. The blocks and the contents within them are protected by cryptography, which ensures that previous transactions within the network can neither be forged nor destroyed (i.e. they are immutable). In this way, blockchain technology allows a digital currency to maintain a trusted transaction network without relying on a central authority. It is for this reason that digital currencies are considered to be “decentralized.”
Digital Assets
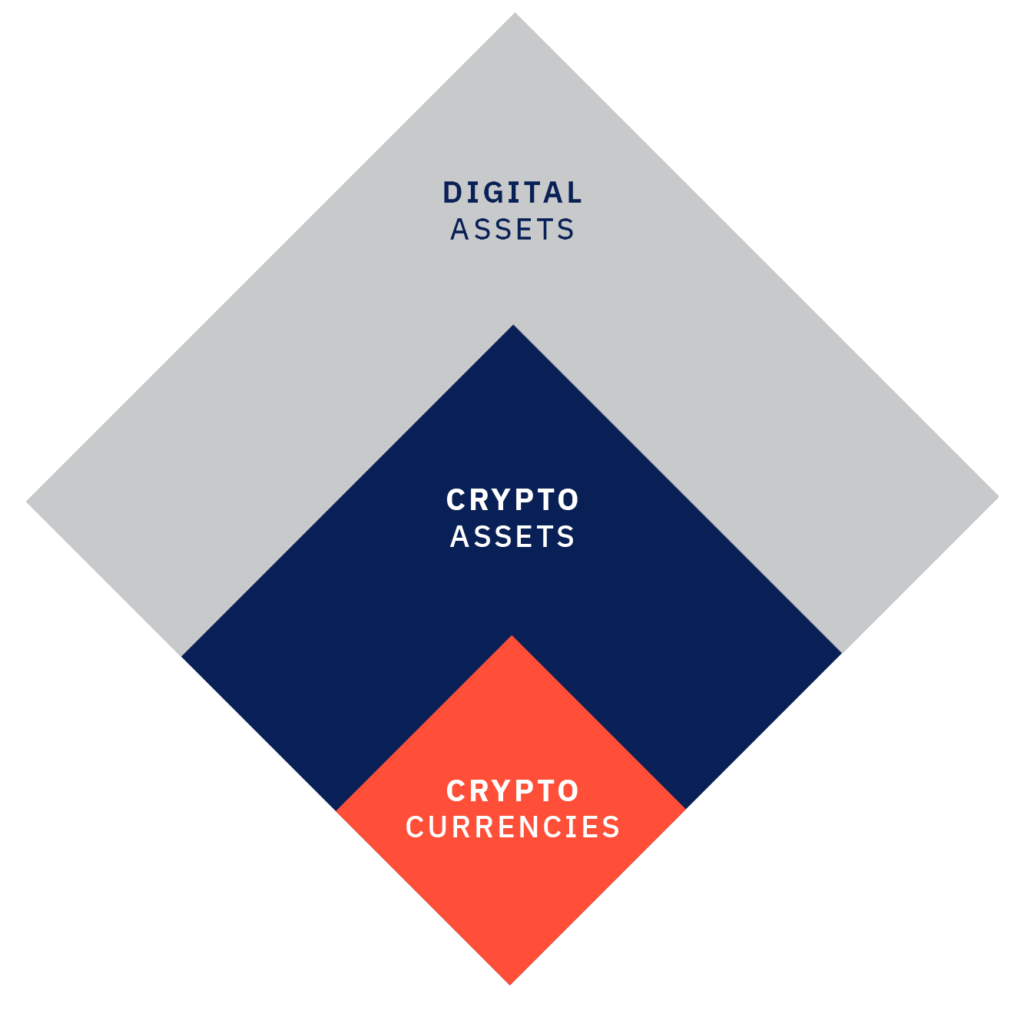
“Digital assets” represent an asset class, and a very general term. To put it simply: if something has value and is in digital form, it is a digital asset. Its examples range from digital media, such as backing songs produced and ready to be sold to singers, to eSports or video game accounts. It also includes a whole spectrum of digital assets which may be more precisely referred to as “crypto assets” or “tokens”.
Crypto Assets
A crypto asset is any digital asset which uses cryptographic technology to execute and secure transactions, manage the creation of additional units, and verify the transfer of assets. Crypto assets are underpinned by a blockchain to maintain a decentralized, and immutable account of transactions. These are decentralized assets with no governing body. As such, all crypto assets are digital assets, but not all digital assets are crypto assets.
Crypto assets can be further divided into more specific forms of assets, one of which being cryptocurrencies which will be mentioned later. Most people consider the terms cryptocurrency and crypto asset interchangeable but there are examples of assets that don’t qualify as a currency. Security tokens, utility tokens, and non-fungible tokens are such examples:
- Security tokens are a crypto asset that is offered as a means of raising funds for a company and pertains to an underlying asset that it may be exchanged for at a later date. This is usually shares, and investors in security tokens benefit from the security and efficiency of the blockchain, whilst also being protected by the regulations the token falls under.
- Utility tokens, another crypto asset that isn’t qualified as a cryptocurrency, generally give the user exclusive rights, such as preferential treatment, or access to utilities/functions that aren’t available to non-holders. Unlike security tokens, the value of these tokens does not directly correlate with the value of the company.
- Non-fungible tokens are a special kind such that, as the name suggests, each token is unique and its characteristics are defined by its respective smart contract. One token’s qualities will vary from another, and a non-fungible token can represent special rights to a physical asset, a digital asset, ownership rights, or anything else that can be thought of. The scarcity of and demand for a non-fungible token’s characteristics are what give it value.
To conclude: As there are so many different types of assets that can be tokenized, crypto assets is a better term to describe the whole category of crypto-related (abstract) objects with value than cryptocurrencies. The difference between a digital asset and a crypto asset is that a digital asset can exist in many non-physical forms, but crypto assets is a term that specifically describes assets that are stored on and operate under DLT.
Cryptocurrencies
A cryptocurrency is a digital or virtual currency that is secured by cryptography, making it nearly impossible to counterfeit or double-spend. Many cryptocurrencies are decentralized networks based on blockchain technology which uses a common shared immutable record of all transactions between all users. A defining feature of cryptocurrencies is that they are generally not issued by any central authority, rendering them theoretically immune to government interference or manipulation.
Coins vs. Token
Two terms that are often mentioned in connection with cryptocurrencies and mistakenly considered to be the same: Coins and tokens. Let’s take a look at the differences:
Unlike tokens, which use existing blockchains such as Ethereum, cryptocurrencies are based on a blockchain developed specifically for the currency. Furthermore, the areas of application differ:
- Coins are structured as a currency and therefore count into the category of cryptocurrency. They pursue three main functions: Money transfer, store of value and representing a unit of account.
- Tokens on the other hand are considered crypto assets but are not cryptocurrencies. They pursue various areas of application, the most common of which are: Activation of features on a (decentralized) platform or representation of physical assets, a process called tokenization.
Cryptocurrencies’ most famous example
Now that we have clarified the differences between coins and tokens, let’s take a look at an example of cryptocurrencies.
Bitcoin is by far the most popular and well-known of all cryptocurrencies, with every other cryptocurrency being collectively referred to as altcoins (“alternative coins”). It follows the ideas set out in a whitepaper by the mysterious and pseudonymous Satoshi Nakamoto who created the technology and whose identity remains unknown to this day.
Before Bitcoin, there had been other attempts to create a cryptocurrency, all of which had failed due to their inability to overcome the double-spending problem. Bitcoin was a revolution because it solved the double-spending problem with the concept of mining and the new technology of a chain of blocks – the “blockchain”.
Mining is the process of transaction confirmation in the course of more Bitcoins are created. It is a process carried out by the users of the network on the decentralized ledger. In the case of Bitcoin, the ledger is a safe book where miners account for all the information about the transactions.
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDC)
With the advent of Bitcoin and altcoins, banks and governments have become more and more nervous over the future implications and possibilities arising from DLT and decentralization. Banks are therefore trying to take steps to prepare for a world heading towards decentralization with the notion of Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs). A central bank digital currency (CBDC) would use digital tokens and blockchain technology to represent a country’s official currency. Unlike decentralized cryptocurrency projects like Bitcoin, a CBDC would be centralized and regulated by a country’s central bank. While several governments are looking into the viability of creating and issuing CBDCs, no country has officially launched such a currency.
Stablecoins
One of the issues with cryptocurrencies that can deter many people is its volatility and lack of stability. Stablecoins are a more recent development in the cryptocurrency world with its value being tied to some external reference. They are cryptocurrencies backed by much more stable assets such as fiat currencies or commodities, meaning they retain all the normal benefits of a cryptocurrency whilst having a lower level of volatility. They can also be stabilized through other more complicated means. For example, the stablecoin Ampleforth is algorithmically maintained – whenever the value of this cryptocurrency goes above or below 5%, a process known as a “rebase” will either increase or decrease the amount of Ampleforth in circulation, in an effort to keep the value of one of its units as close to $1 as possible. Since rebasing is proportional across all wallets, holders of the currency always maintain the same share.
Now that we know the different types of digital assets and their specifics, we’re ready to explore the ways digital assets are impacting today’s financial world. Stay tuned for Part 3, where we’ll dive into topics like “The New Era of Crowdfunding” and “Smart Contracts”.