One of the most popular DeFi apps is Aave, a decentralized lending protocol where users can lend and borrow crypto assets.
In this beginner’s guide, we’ll explore what Aave is, how it works under the hood, its key features, risks to know, and how to get started using this innovative platform. By the end, you’ll have a solid understanding of Aave and its role in the exploding DeFi landscape. So let’s get started and decode this game-changing financial application!
What is Aave?
In general, Aave is an open-source, non-custodial protocol that allows people to lend and borrow cryptocurrencies through decentralized finance (DeFi). Essentially, it provides a peer-to-peer money market for cryptocurrencies, removing financial middlemen from the equation.

Originally built on the Ethereum blockchain, Aave has expanded to other chains like Polygon to improve transaction speeds and reduce fees. At its core, Aave uses smart contracts to enable the lending and borrowing of digital assets without the need for a centralized authority.
Lenders can deposit supported cryptocurrencies into Aave liquidity pools to earn passive income as interest. Borrowers can then use their crypto as collateral to take out a loan in the form of another cryptocurrency such as stablecoins. The loans are overcollateralized to protect lenders in case the market crashes. Through automation, Aave streamlines lending in a transparent and decentralized manner.
By providing an easy way to earn interest on holdings as well as access loans, Aave has become a leading DeFi protocol with billions of dollars deposited. It exemplifies the potential of decentralized apps to disrupt traditional finance.
Aave’s History and Founders
Aave was founded by Finnish entrepreneur Stani Kulechov in 2017 under the name ETHLend, one of the first decentralized lending protocols on Ethereum. Kulechov developed the platform as part of his law thesis exploring the potential of blockchain technology and smart contracts for peer-to-peer finance.
ETHLend held an initial coin offering (ICO) in 2017, raising funds through its LEND token. However, the platform saw limited adoption over the next couple years. In 2020, Kulechov rebranded ETHLend to Aave, improving the protocol and swapping LEND for an upgraded ERC-20 token known as AAVE.
This rebrand marked a new chapter for the project. Aave switched from an order-book system to automated pool-based lending and added key features like flash loans. The team also focused on multi-chain expansion and real-world asset integrations.
The improved Aave protocol quickly gained traction in DeFi, becoming one of the top lending platforms. The total value deposited has soared to over $10 billion as of 2022. Through Kulechov’s persistence and innovation, his academic research project evolved into a leading decentralized finance application.
How Aave Works?
To understand ‘What is Aave’, it’s crucial to grasp how it operates. Instead of direct peer-to-peer lending, Aave uses pooled funds for lending and borrowing. Users who want to earn interest can deposit their cryptocurrency into these pools, providing liquidity. Borrowers can then draw loans from these pools collateralized by their own crypto.
For example, Jane deposits 10 ETH into the ETH lending pool. This contribution gets recorded by a smart contract and minted into aTokens, let’s say 10 aETH, representing her share of the pool. These aTokens continuously accrue interest for Jane.
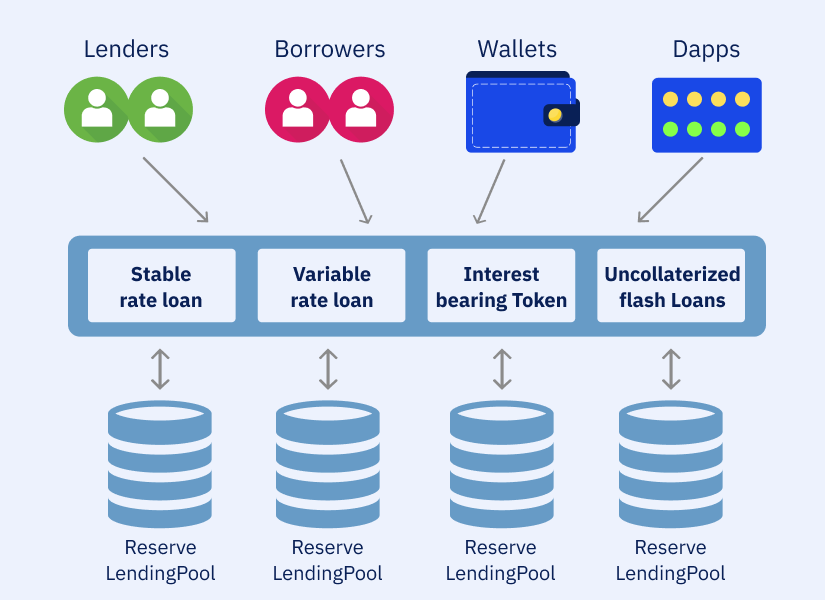
Robert wants to borrow 5 ETH. He puts up 15 ETH as collateral into a smart contract and takes 5 ETH from the lending pool that Jane contributed to. He now owes 5 ETH plus interest. The collateral protects lenders in case Robert defaults.
Loans have flexible repayment, but interest compounds over time. Interest rates adjust algorithmically based on the utilization ratio of assets in the pools. Higher demand increases rates to incentivize more deposits.
If the value of collateral drops below a threshold compared to the loan, the collateral can get liquidated to repay the debt. Liquidations protect lenders from market volatility.
By automating lending with smart contracts, Aave removes the need for manual vetting and intervention. The protocol manages everything, providing a transparent peer-to-peer alternative to traditional finance.
Borrowing and Lending with Aave
Now that we’ve tackled ‘What is Aave’, let’s delve into the core functionalities it offers. Aave offers a straightforward way for crypto holders to earn interest through lending or gain access to credit lines by borrowing. As a lender, you simply need to deposit cryptocurrency like ETH or stablecoins into the protocol’s liquidity pools. Your funds will start automatically earning interest based on current rates.
Interest accrues by the second, credited in real-time. There’s no fixed term, so you can withdraw your money plus interest anytime. To borrow on Aave, you must put up collateral worth more than the loan amount. This “overcollateralization” protects lenders. The collateral can be crypto or even real-world assets like invoices. You can then borrow assets including stablecoins, with interest rates starting around 3-5%.
Borrowers have no set repayment deadline but interest compounds over time. Aave calculates a “health factor” measuring your collateral ratio compared to the loan. If your health factor drops too low, a partial liquidation of collateral kicks in to repay part of the loan to maintain a safe ratio.
Aave’s Key Features
Beyond basic lending and borrowing, Aave packs in advanced features that make it a versatile DeFi platform. Let’s explore some of the protocol’s most unique capabilities.
Flash Loans – Lightning Fast Financing
Flash loans allow users to instantly borrow crypto without any collateral, as long as the funds are returned by the end of the transaction. This works because the loan is atomic – if not paid back, the entire transaction reverses as if nothing happened.
These “one block loans” are useful for arbitrage trades across decentralized exchanges. Traders can borrow large amounts, execute profitable swaps, and pay back the loan plus fees in seconds.
To take a flash loan:
- Call the smart contract and specify the amount to borrow
- The contract loans the funds to your connected wallet
- You can now trade, swap, or interact with other protocols
- Before the transaction confirms, repay the loan within the code
If the repayment fails, the flash loan is canceled. Aave charges a 0.09% fee on these loans, paid to liquidity providers. With removing collateral requirements, flash loans unlock new capital efficiency for advanced users.
Staking – Earn Passive Rewards
Aave lets users earn yield through staking the AAVE token. When you stake AAVE, it provides security to the protocol in case of shortfalls. In return you receive staked AAVE or stkAAVE equal to your stake.
stkAAVE can be used the same as regular AAVE for governance or lower borrow fees. But it also continuously accrues rewards that can be claimed in the form of AAVE tokens.
Stakers help safeguard the protocol and earn attractive yields up to 10% on their holdings. However, staked tokens are locked for at least 7 days before they can be withdrawn.
Real World Assets – More Collateral Options
Aave provides the ability to use real-world assets as collateral for loans, not just crypto. These “RWAs” are tokenized versions of actual assets like invoices, rental payments, royalties, and more.
For example, a business could tokenize $100,000 of unpaid invoices. This gets minted as 100,000 wBTC, which can be used as collateral to borrow stablecoins on Aave.
When the invoices get paid, the business unlocks their wBTC. By broadening acceptable collateral, Aave creates new liquidity streams for real-world financing.
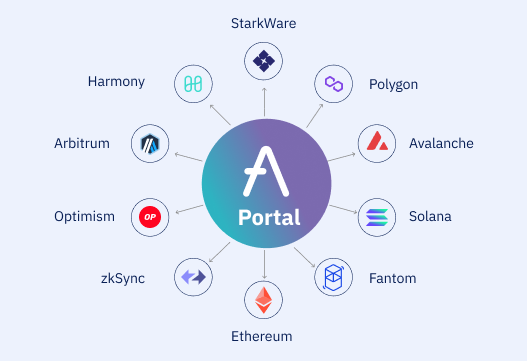
Interoperability – Cross-Chain Flexibility
Aave doesn’t just operate on Ethereum – it’s implemented across over 10 different blockchain networks. This interoperability lets users access Aave’s services on various chains.
For instance, you could lend ETH on the Ethereum network and borrow MATIC on Polygon to take advantage of faster and cheaper transactions. Bridging assets between chains is easy.
The cross-chain nature improves flexibility, enhances accessibility, and lets users optimize operations across blockchain ecosystems.
Safety Module – Insurance Fund
Aave has a “safety module” containing staked AAVE tokens to provide insurance in case of shortfalls, such as undercollateralized loans. If a shortfall event occurs, the protocol automatically mints and sells AAVE from this module to cover the gap.
The safety module acts like a pooled insurance fund to mitigate risk. In return for providing security, contributors to this pool earn additional AAVE rewards funded from protocol fees. The various safety measures minimize risks and instill confidence in the decentralized system.
The AAVE Token
The AAVE token is the backbone of the Aave ecosystem, enabling community governance and incentivization. AAVE is an ERC-20 utility token required for certain activities on the protocol.
Firstly, AAVE can be staked to secure user funds in the safety module, earning stakers rewards in return. Staking also gives voting rights to influence protocol changes. Each AAVE equals one vote, taking the community’s pulse on upgrades.
Users who lock up AAVE as collateral when borrowing enjoy lower interest rates than those using other cryptocurrencies. This incentivizes demand for the token among borrowers.
Additionally, Aave buys back AAVE using the protocol fees it collects, then burns the tokens. This gradually reduces the circulating supply, currently around 13 million tokens. Scarcity plays a role in AAVE’s market value.
While users aren’t required to hold AAVE to use Aave, those deeply involved have incentive to gain influence over governance decisions. Additionally, staking and reduced fees provide monetary value.
As the protocol grows, AAVE capture’s Aave’s increasing success. The token unlocks greater participation and value accrual aligned with the network’s prosperity.
Risks of Using Aave
While Aave unlocks new opportunities in decentralized finance, it also comes with certain risks that users should consider.
Firstly, smart contracts powering Aave could contain bugs or flaws resulting in loss of funds. Though the code is open-source and audited, issues can still slip through.
Additionally, the high collateral requirements and liquidation procedures protect lenders but can harm borrowers in volatile markets. If asset prices crash, borrowers may get positions prematurely liquidated at unfavorable rates.
There is also no insurance or recourse for lost or improperly sent funds. One mistake in typing a wallet address means deposited funds disappear forever.
Finally, Aave depends on the stability of blockchain networks like Ethereum. If there are problems with a underlying blockchain, transactions and smart contracts may be disrupted.
While Aave’s track record so far is strong, users should be aware of these risks before depositing significant capital. As with any DeFi protocol, caution is warranted to avoid losing money due to technology or market fluctuations.
Getting Started with Aave
Ready to start using Aave? Here’s a quick guide to get up and running:
- First, you’ll need to install a crypto wallet like MetaMask as this connects you to the Aave protocol. Make sure to securely back up your seed phrase. Then you can purchase ETH or another cryptocurrency on an exchange.
- Next, navigate to the Aave website and connect your wallet. You’ll see your full token balances and options to supply assets to start earning interest. Click supply and approve the transaction to deposit tokens into the lending pool.
- Once your funds are pooled, you’ll receive aTokens representing your share. These increase in number as interest accrues. You can track your lending positions and see associated information like interest rate, total supply, and your share.
- To borrow, click on the asset you want to borrow and enter the amount. You may need to approve your wallet first. Next, you’ll be asked to supply collateral worth more than the borrow amount. Confirm the transaction and the borrowed crypto will show in your wallet.
Remember loans accrue interest over time so aim to repay as soon as possible. You can repay at any point by withdrawing the borrowed amount from your wallet to the protocol.
Start small until you get the hang of managing lending and borrowing positions. And be cautious of sharp price declines that could lead to quick liquidations. Aave opens up decentralized finance – just tread carefully as a beginner.
Ready to be a part of the decentralized finance revolution? Embark on your DeFi journey today by getting hands-on experience with Aave. Buy Aave and start exploring a world of financial possibilities devoid of traditional banking hurdles.

Conclusion
Aave provides a pioneering peer-to-peer crypto lending platform through smart contracts. Users can earn interest on holdings, access collateralized loans, and utilize flashy new features like flash loans. Backed by the AAVE token, it offers community governance and incentives. While risks exist, Aave displays the potential of DeFi to transform finance.
With continuous growth and development, Aave sits at the forefront of decentralized lending. It delivers an automated, transparent banking alternative for handling cryptocurrencies. The DeFi movement is just getting started, and Aave aims to lead the charge.
Whether you want to Buy Aave with Apple Pay or Buy Aave with PayPal, beginning your journey into decentralized finance has never been easier or more convenient. Choose your preferred payment method and step into a world of financial possibilities with Aave today!
Moreover, if you’re curious about the financial trajectory of Aave? Discover what the future might hold by diving into our detailed analysis in the post, “AAVE Price Predictions (2023 to 2030)“. Gain insights into Aave’s potential growth over the next decade and make informed decisions on your DeFi investments.
FAQs
Aave is an open-source, non-custodial DeFi protocol that allows users to lend and borrow cryptocurrencies without the need for middlemen. Unlike traditional finance, Aave operates on blockchain technology, enabling peer-to-peer transactions through smart contracts, eliminating the need for centralized authorities.
Flash loans are unique features of Aave that allow users to borrow crypto instantly without collateral, provided the loan is repaid by the end of the transaction. If the loan isn’t repaid, the entire transaction is reversed, making it as if it never happened. These loans are primarily used for arbitrage opportunities across decentralized exchanges.
The AAVE token serves as the backbone of the Aave platform, enabling community governance, staking for security, and incentivization. It can be used to vote on protocol changes, stake in the safety module for rewards, and when used as collateral, it offers borrowers reduced interest rates.
Aave has implemented a “safety module” that contains staked AAVE tokens to act as an insurance fund in case of shortfalls, such as undercollateralized loans. This module helps mitigate risks and provides an added layer of security for the platform.